Former Google employee Kaspar Szymanski has just talked about Google spam filters and shared his expertise about how to recover websites from all kinds of Google penalties. Kaspar had been part of the Google Search Quality team for 7 years, where he was the driving force behind global web spam tackling initiatives and the public face spearheading Google’s webmaster outreach and communication efforts.
Let’s proceed to what Kaspar said about manual spam actions, filters, bans and penalties.
Kaspar Szymanski: ex-Google web spam hunter and SEO consultant specializing in backlink risk analysis + penalty recovery assistance
The first and the most important recommendation is to read and re-read the Google Webmaster Guidelines. Following the Guidelines will help Google find, index and rank your site, and will assure that your site will not be removed from Google index for violations. Re-reading is really important as Google often updates the Guidelines and a technique that was legitimate yesterday might have become shady today.
What to Do if Google Has Penalized Your Site
Google’s manual action email is not a death sentence. You should remember that all penalties have their period of validity and will not last forever. Besides, the penalty impact may be very different: it may be a tickle with a feather or it may be a real nuclear explosion.
Your first task is to keep calm and investigate.
1. Define the scope
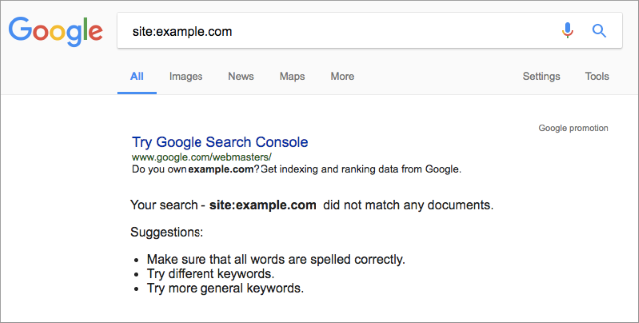
Google may penalize the whole site, a site directory or one site page only. Perform a site:domain search to see if your site is still in the Google index.
If the whole site has been removed from the Google index, you’ll need a lot of work done.
2. Find out the reasons
Google always explains the reason for a manual action via Google Search Console (Google Search Console → Search Traffic → Manual Actions). Be sure to check the Manual Actions sections regularly.
Types of Google Penalties
Google Manual Actions messages always explain what caused a penalty and what should be done to recover from it.
1. Major spam problem
Google may remove the whole site from its index when a major spam problem is found. A major spam problem is a violation of Google Webmaster Guidelines (remember to read them regularly!)
2. Thin content
If a site provides content with little or no value to searchers, Google may remove some parts of the site from the index.
3. User-generated spam
This problem may occur with sites that allow posting links in a comment section with no moderation and without a NOFOLLOW attribute.
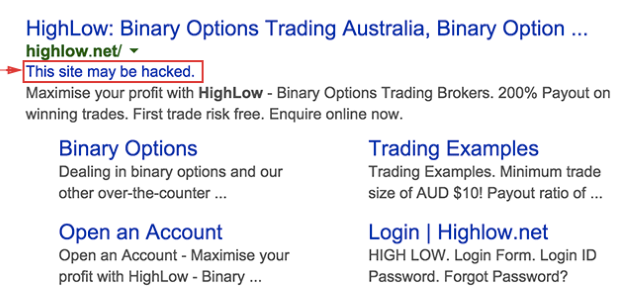
4. Hacked content
Google may notice if your site was attacked by hackers and now promotes malicious content. The worst about this issue is that in the SERPs a “This site may be hacked” notification may be shown for all pages of your site, even those that are OK.
5. Incorrect structured data
Structured data is meant to help Google understand what a site is about. We’ve noticed that adding structured markup greatly improves a site’s visibility and rich snippets attract more clicks in the SERPs. However, some not-very-white-hat SEOers try to use schema to manipulate search results. For example, a brand review with 5/5 stars by 300 people may trigger a Google manual review and spam actions.
6. Selling links
Unnatural outbound links, i.e selling links violates the Google Guidelines and may be a reason for some manual actions applied. Links that are placed to manipulate the Google search results are considered unnatural.
7. Buying links
Unnatural links that point to your site may also trigger a manual action. What looks unnatural to Google:
- Great amount of links that appeared in a short period of time
- Especially if they have keyword-rich anchor texts
- Especially if these anchor texts are commercial (i.e. contains CTA like “buy best socks here”)
How to Recover from a Google Penalty
1. Document
Document what was causing a penalty and carefully note what you are doing to stop violating the Google Webmaster Guidelines. You will need these notes when you send a reconsideration request.
2. Create Unique Selling proposition
If your site is accused of having thin content, Google wants you to not only re-write your content to make it more valuable and unique, but they also want you to create a unique selling proposition. A unique selling proposition is what your business stands for.
3. Remove or NOFOLLOW links
Add a NOFOLLOW attribute to all outbound links that may look suspicious to Google or remove them. Be sure that user-generated content on your site is moderated and NOFOLLOW is added to all links that your users post.
4. Disavow inbound links
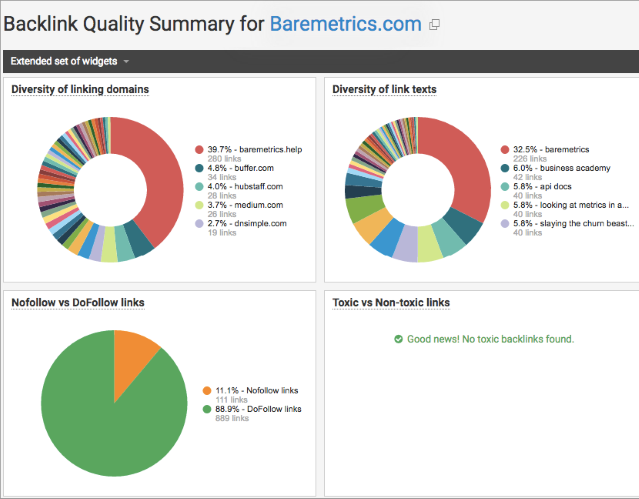
This is the hardest part, because you will need to change other sites, not your own. First of all, carefully investigate your inbound link profile. Things to pay attention to:
- Diversity of linking domains
- Diversity of anchor texts
- Amount of keyword-rich anchor texts
The best tactic is to use a reliable source of link data. I prefer to use the WebCEO Backlink Quality Check as it allows a user to see how many linking domains he or she has, what link texts are used and whether the keyword-rich texts have NOFOLLOW. You can report links you want to disavow directly from WebCEO.
WebCEO has proven to be the best tool to clean up a negative SEO attack or to recover from a Google penguin penalty.
Tips on Making a Google Reconsideration Request
When you’ve removed all the things that caused a penalty, it is time to send a reconsideration request. A reconsideration request is a request to have Google review your site after you fix the problems identified in a manual action notification. Here is where the notes you were taking will help.
- Sign into your Search Console account.
- Make sure you’ve fixed all the issues mentioned in Manual Actions.
- Review Security Issues in Search Console for other possible issues with your site.
- Click on ‘Request a review’ to ask Google to reconsider your site.
Remember that all reconsideration requests are processed manually by real people. Quick tips:
- Be polite
- Explain what you’ve fixed
- Write pithily
- Never say that you will take legal actions against Google (Kaspar says it happens often!)
Usually it takes 2-3 weeks for a request to be processed. However, it is faster at the end of the year, because Google doesn’t do new releases near Christmas.
After Google reviews your site, you’ll receive a message indicating the outcome of your reconsideration request.
1. Request Rejected
This may happen if your site still violates the Google Webmaster Guidelines. Do not panic, read the message carefully and fix everything that is mentioned.
Sometimes Google will even show examples of unnatural links pointing to your site, but it happens rarely (on Christmas, I think).
2. Request Processed
Sometimes after you fix some issues and send a reconsideration request, the manual actions at issue are removed, but other manual actions are applied! In such a case never send angry emails to Google. Just fix the issues and send another reconsideration request.
3. Request Approved
Congratulations! Your site is in Google’s high favor again!