
What new bloggers and site owners might not know is user experience is one of the factors of ranking a website on Google search results.
And especially now that most of the world is going online for all their needs, ranking higher on search results is a must. This means businesses are faced with the challenge of creating a user-friendly website and achieving their short- and long-term marketing goals.
Seasoned marketers know that becoming an SEO specialist involves more than writing long-tail keywords and meta tags. So how can you make sure user experience on your site actually helps boost your rankings? Read on to learn 10 essential tips to create an SEO-friendly website with easy site navigation for users.
1. Check the Site Health of Your Website Regularly
Conduct an assessment of analytics on your site before you overhaul it completely—this way you’ll see what’s doing well and then only focus on what needs improvement. Measuring product analytics in this case involves analyzing how users find, engage, and interact with your website.
You can start by identifying traffic trends and pain points in the customer journey throughout your website in order to optimize the user experience. There are several free tools you can use to measure your site health, including GTmetrix, Google Pagespeed, and WebCEO’s Website Auditor.
The great part about these tools is that they even point out which elements may be causing your site navigation and performance to be acting poorly than average, as well as your next steps to solving them.
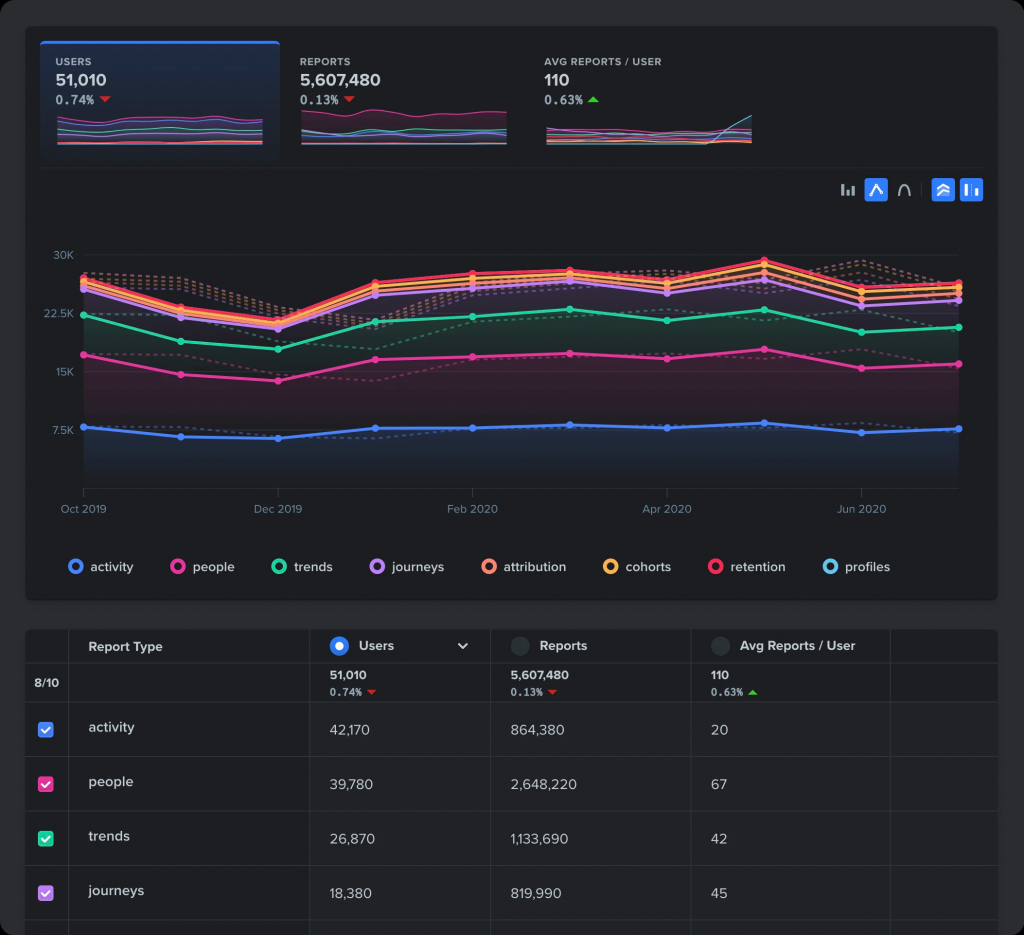
(Source: Woopra)
2. Map Out Your Site Structure
There is an absolutely essential step in creating a good (both for users and SEO) site navigation: planning out your content hierarchy. What makes it so? Because organizing your site’s content into a logical structure makes it easy to navigate for humans and crawlers alike. It greatly improves the user experience, and you can imagine what the opposite does to UX.
You wouldn’t want your visitors to click out immediately just because they can’t find their way around your site. A standard horizontal navigation menu on the top or a vertical navigation menu on the left side of the webpage can do wonders for making your website easier to use.
Consider structuring your website according to group topics of content. This way, search engines will easily find and identify the ranking and importance of pages on your site.
Aside from content groupings, consider adding main pages like sales pages or service pages as top pages for your menu, so they’re easily available on your header or your footer. This will also be easier for you to keep track of website performance if your content is structured.
Before you start building or reorganizing your site, lay out a plan of the site structure first. This way, you can place and add content anytime without worrying about missing or breaking something or changing the site drastically.
(Standard horizontal navigation bar on the top of WebCEO’s home page.)
Another way to improve your content hierarchy is to express it in the pages’ URLs. For example, let’s say you run an online store. Your products will be sorted into categories, and so a product page’s URL will be structured like this: https://onlinestore.com/category/product. Naming your site’s pages and subdirectories in this manner makes them descriptive and easy to understand, whether you are a human or a robot.
Lastly, don’t make your hierarchal website structure too deep. A flat URL structure ensures all content on a site can be found quickly, so a three-step hierarchy like home page -> category -> product is usually the most efficient and optimal for SEO. However, a deeper structure can be just as good when it’s done right. Adding more steps can result in longer, but more descriptive URLs. This approach is recommended for sites with complex content (for example, related to science or medicine) where having more context is helpful.
3. Create a Schema Markup
Simply put, schema markup is a form of data added to a webpage so that search engines are able to better understand the content of this particular page. A rich snippet shows up on search engine results pages (SERPs) when you add schema markup on a webpage.
Rich snippets can feature descriptions, photos, reviews, ratings, contact details, and other content about the webpage based on the search result.
Aside from having organized data, having schema markup is an effective way to ensure that Google can read the content on your site and rank you higher in search results. Plus, you can improve click through rates on your site as well.
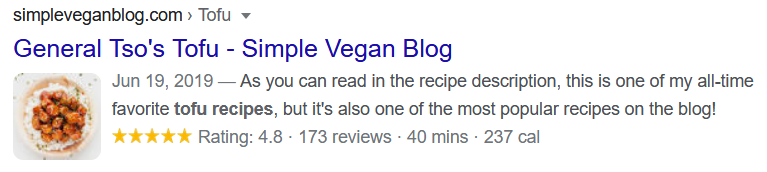
You can see average ratings as schema markup.
4. Prioritize Your Users, Not Search Engines
As a marketer, your priority is to create content that is valuable to the user. Ranking high on search engine results comes afterwards. Search queries are usually classified as the following:
- Transactional. Users want to do something on your site (book a flight, purchase an item, etc.)
- Navigational. Users want to go to a particular web page
- Informational. Users want to know something on your site (contact details, shop hours, FAQs, etc.)
When users value your content, your search ranking will also increase and your website will be visible to more visitors. Remember that search engines reward websites that show they understand their users—so focus first on how your users are using your site, and then search engines will reward you later.
5. Reduce Your Page Load Time
Marketers are competing for the customer’s attention. The average attention span of a visitor on your website is at 8 seconds, and 47% of consumers expect a web page to load in 2 seconds or faster. If the website takes more than 3 seconds to load, chances are 33% of visitors have left by then.
You can reduce load time on your web pages by optimizing images and media, prioritizing visible content, enabling browser caching, and minimizing redirects on your site. Investing in a cloud storage service is also an advisable way to reduce page load times. Cloudwards evaluated that half of the top 12 services take only 25% longer to upload data and 27% longer to download data than expected.
6. Make Your Website Mobile Friendly
You can’t underestimate the importance of optimizing your website for mobile users. People are spending a lot of time on their smartphones and tables. At least 52.6% of web traffic is generated through mobile devices and 51% of internet users already use their mobile devices to shop online.
Optimizing your website for mobile provides users with an easier way to navigate your site. You should design your mobile website with touch devices in mind. Avoid adding small click through links and opt for visual icons so users will know where each click will take them. Remember, always add a visible Call to Action on the pages.
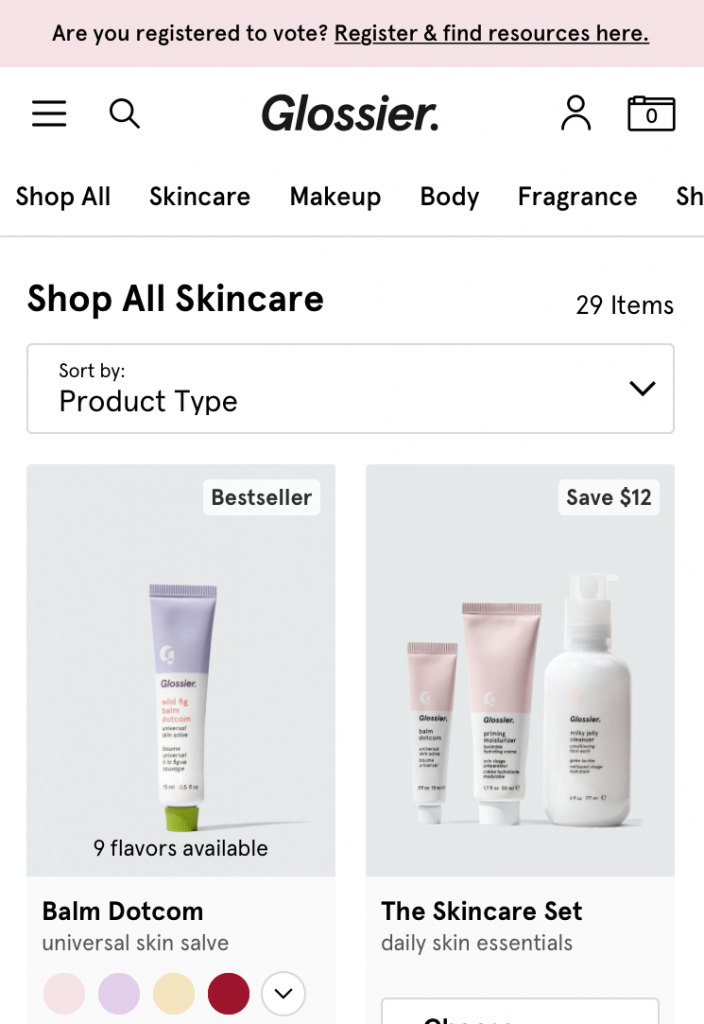
(Glossier’s mobile website features visual cues and organized categories.)
7. Apply the Topic Cluster Model for Your Content
Topic clusters use hyperlinks to group different pieces of content which are related to a general topic on your website. By organizing topic clusters, your target audience will easily see your posts on your website. That way, you can also increase traffic and engagement on your site.
But long-tail keyword density isn’t just the key to ranking high on search results. Google prioritizes the quality of information provided by your content. The more relevant and informative your content is to users, the higher it appears on search results.
Topic clusters help solve that exact need. By focusing your content around broad topics and creating highly detailed posts on specific things under said topic, you can cover as much relevant information as possible. You also allow users to stay on your site and find other posts around the same topic—which in turn boosts your user experience and ultimately rankings.
8. Make Your Labels Clear and Specific
Navigation labels should be clear and descriptive. Every business has a product page or a page for their mission.
Be direct and keep the customer interested by using descriptive navigation labels. If your website is easy to navigate, customers will be more engaged and bounce rates will reduce. You can use online SEO tools to help you track your rankings and choose the right keywords for your website labels.
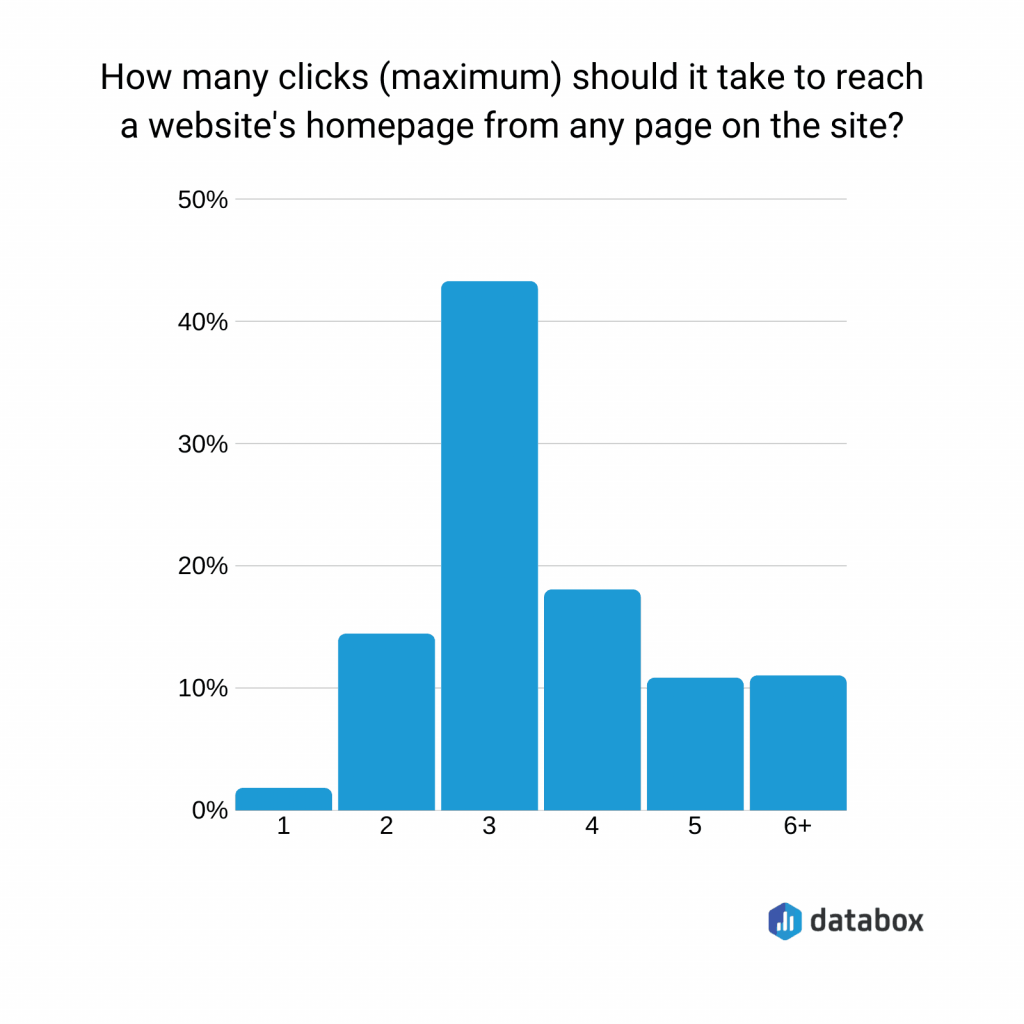
(Source: Databox)
9. Avoid Dropdown Menus
You should avoid dropdown menus if you want to optimize your website for SEO. Search engines find it difficult to crawl through dropdowns, and frankly, users don’t like clicking through lots of links.
Dropdowns can also decrease visits on top level pages since users often skip to the options in the sub pages.
If you must use them on your site, make sure they are activated by touch for mobile users or by hovering your mouse for desktop users. Keep the multilevel navigation simple with no more than two layers of dropdown options.
10. Include Breadcrumbs
Like Hansel and Gretel in the woods, you should leave breadcrumbs—or short navigation menus—for your visitors so they can easily navigate around your site if they’re on a page that’s already far from the homepage.
Breadcrumbs make your website SEO structure cleaner and much more efficient to navigate. They usually appear at the top of your content, right beneath the header. Users can easily discover related content by clicking through the previous breadcrumb, and these can show off your site’s easy navigation.
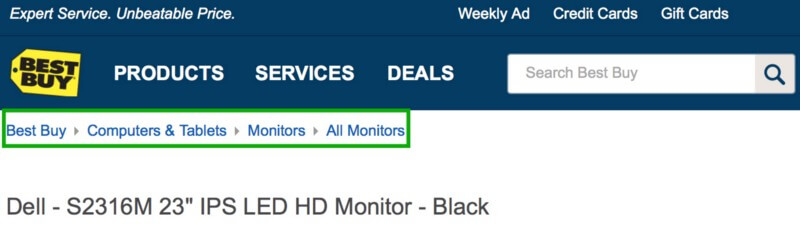
(Source: UserSnap)
Key Takeaways
It takes more than just a keyword strategy to start ranking higher up on search engines. A well-designed and SEO-optimized website leads to a better user experience, and eventually more conversions for your business. After all, when Google sees your users love your site, they’ll reward you for it. Sign up for WebCEO to access the only tools you need to optimize the user experience for your customers.


